Refrigerators are essential electronics in many homes. They keep your drinks chilled and preserve your leftovers. Therefore, the kitchen is generally incomplete without a fridge. You may as well want to add a wine fridge and not know how much energy it will consume.
However, it may add a considerable charge to the electric bill. So, how much electricity does a refrigerator use? Will adding a fridge to your kitchen make you pay larger electric bills? Let’s go through this article to get a hint.
How Much Electricity Does a Refrigerator Use?
A typical household refrigerator consumes 350–780 watts. The type of refrigerator you own, its size and age, the ambient temperature in the kitchen, and where you have it all affect how much energy your refrigerator uses.
An Energy-Star-certified refrigerator, for instance, operates up to 9% more efficiently than other models and a lot more efficiently than older appliances. A full-sized kitchen refrigerator uses more energy than a small mini-fridge.
Refrigerators cycle on and off, meaning they do not continuously use power. They only consume power when running. However, when not running, they consume no power.
Estimate Your Refrigerator’s Energy Consumption
If you’re curious, there is a simple method to determine the amount of electricity your refrigerator consumes. Look for the number of volts and amps on the sticker inside your refrigerator to find out how many watts it has. Then, multiply these values by the number of watts your refrigerator consumes.
For instance, an old refrigerator might have 115 V, 6.5 amps, and 747.5 watts overall. On the other hand, a more recent Energy Star-certified refrigerator may have 117 V and 3.3 amps for a wattage of 379.5.
How To Calculate The Average Refrigerator Wattage
There are three easy ways to determine the energy usage of a refrigerator.
a) Check the Volts and Amps Sticker
Appliances frequently feature a sticker on the back that lists the unit’s voltage and amperage. Simply multiply volts by amps to get watts.
Image source: auditoria.com
You may realize that your refrigerator uses 386 watts, for instance, if the sticker states that the voltage is 117 and the amps are 3.3.
b) Use the Energy Star Rating
The information on Energy Star labelling about an appliance’s electricity usage is useful. Less energy will be used by more efficient models, which will cut electricity costs. This is a great approach to compare the energy consumption of one appliance to those of other comparable models.
Image source: jagran.com
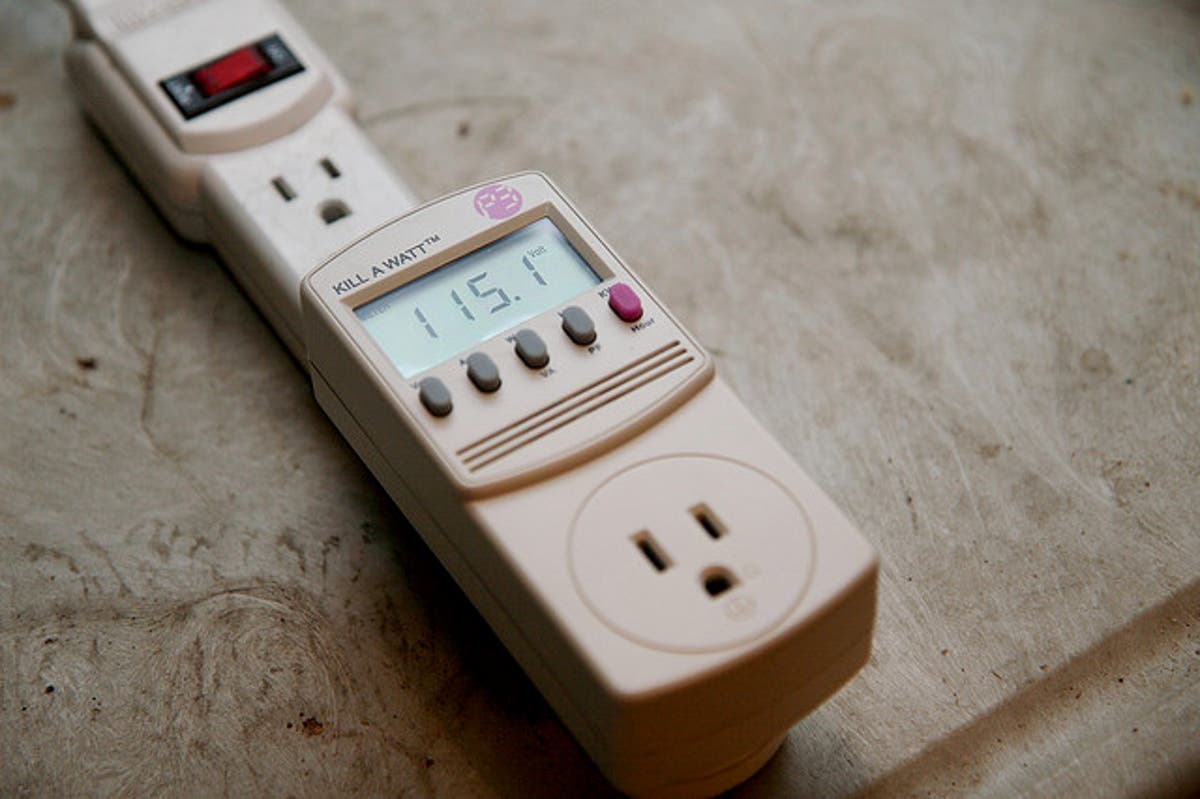
c) Purchase an Energy Meter
An energy meter measures how much power a certain machine consumes when the device is directly plugged into a refrigerator. They typically have a few distinct modes and can calculate the total energy consumption over time in kilowatt hours and the usage in the present kilowatts.
Image source: greenlivingideas.com
Energy meters differ from an in-home energy display, which typically measures the overall amount of energy used in the home and is device-neutral.
How to Improve Your Refrigerator’s Energy Efficiency
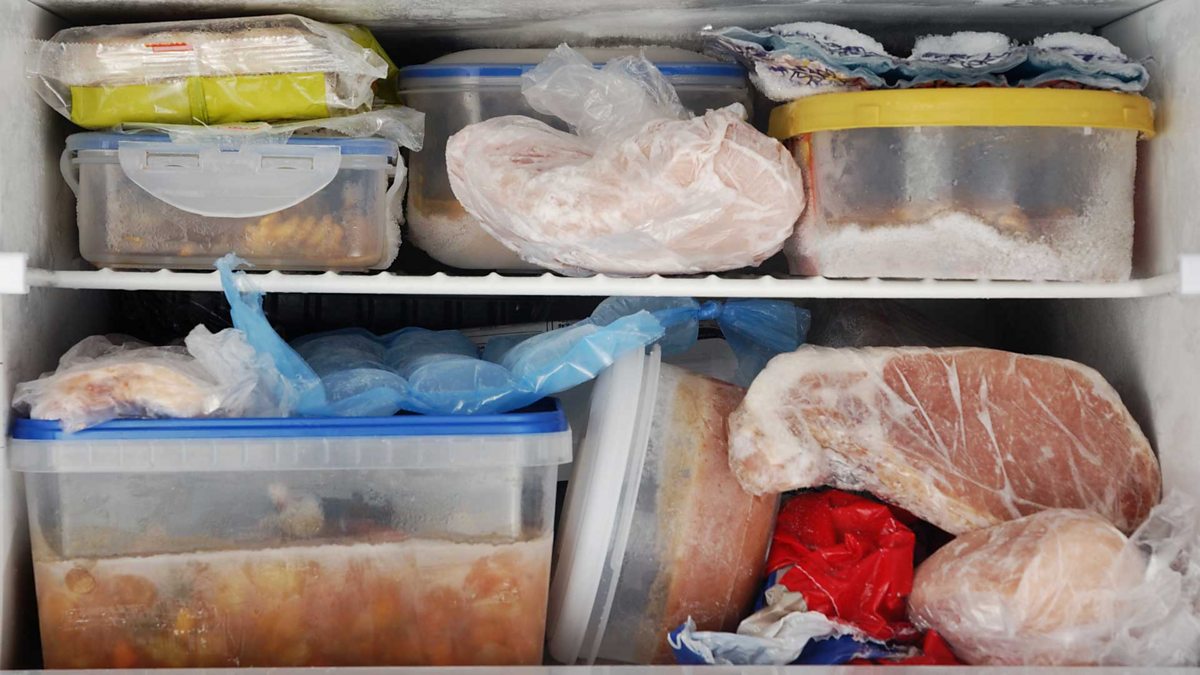
a) Fill the Freezer
When fully stocked, the freezer operates at its peak efficiency. Fill any available space in the freezer with extra ice for cold beverages or cold packs for summertime picnics.
First, put the foods in the best freezer bags, then place them neatly in the freezer. It is beneficial during a blackout as full freezers keep food frozen longer in the event of a power loss.
Image source: bbc.com
The refrigerator is different altogether; it requires airflow to maintain food at a consistent temperature. When food is packed too closely in a refrigerator, certain items freeze and become overly cold, while others don’t stay cold enough to be stored properly.
To keep food fresher longer, allow the refrigerator to air. This does not mean that it should be empty. It would be best to fill up to around two-thirds of its capacity.
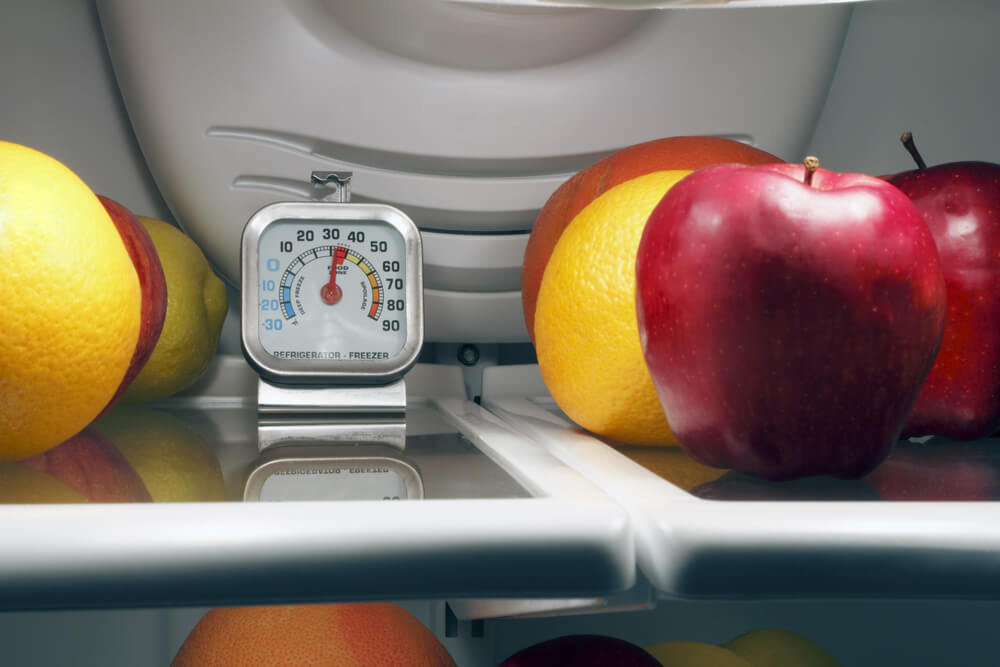
b) Track Temperatures
Tracking the temperatures of a refrigerator or freezer might be crucial to cost-effectiveness. Temperatures that are too low squander energy, while those that are too warm hasten the deterioration of food.
Image source: lovefoodhatewaste.com
Be careful not to have the thermostat set too low. Freezers should be adjusted to -18°C, while refrigerators should not be below 5°C. When the seasons change, pay attention since a temperature setting that works well in the wintertime might need to be changed in the summer.
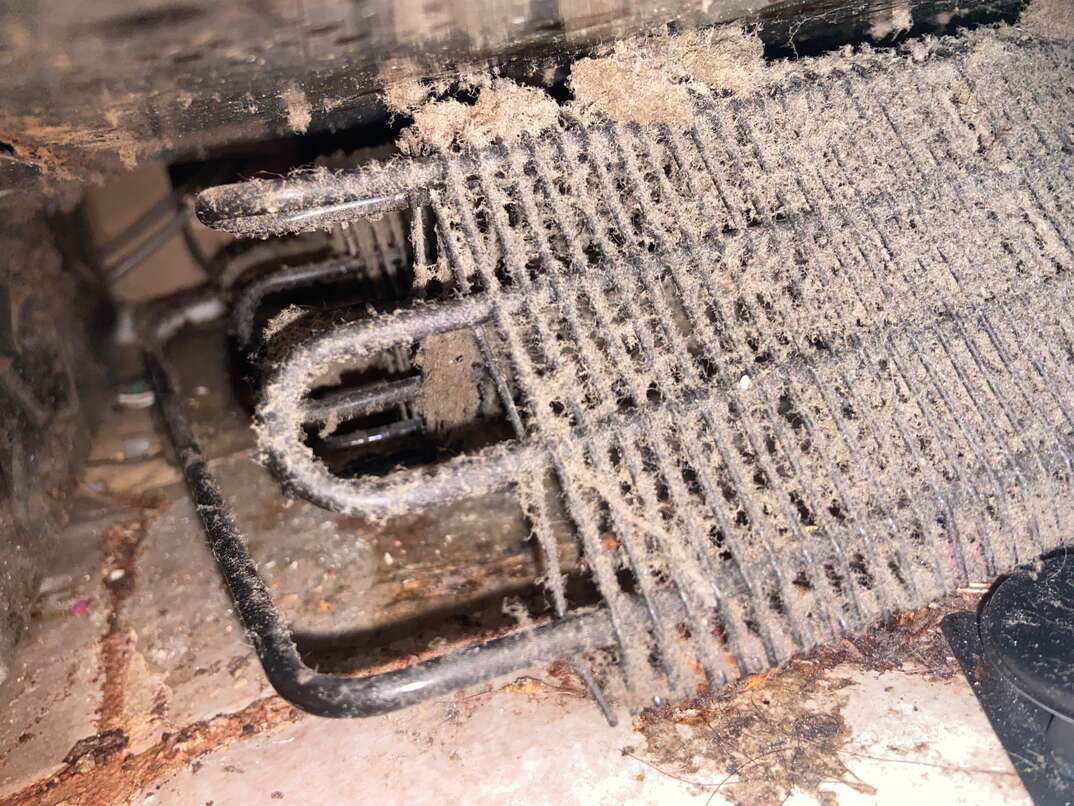
c) Check the Condenser Coils
Condenser coils perform the labor-intensive task of producing cool air, but if their surface is covered in dust or grime, they are unable to radiate heat effectively. If dirty, the condenser coils behind or below the refrigerator should be cleaned with a coil brush or a vacuum cleaner.
Image source: elocal.com
Condenser coils should be cleaned at least two to three times annually. Maintaining clean coils will increase the useful life of your appliance and reduce operating costs because they cool the air more efficiently.
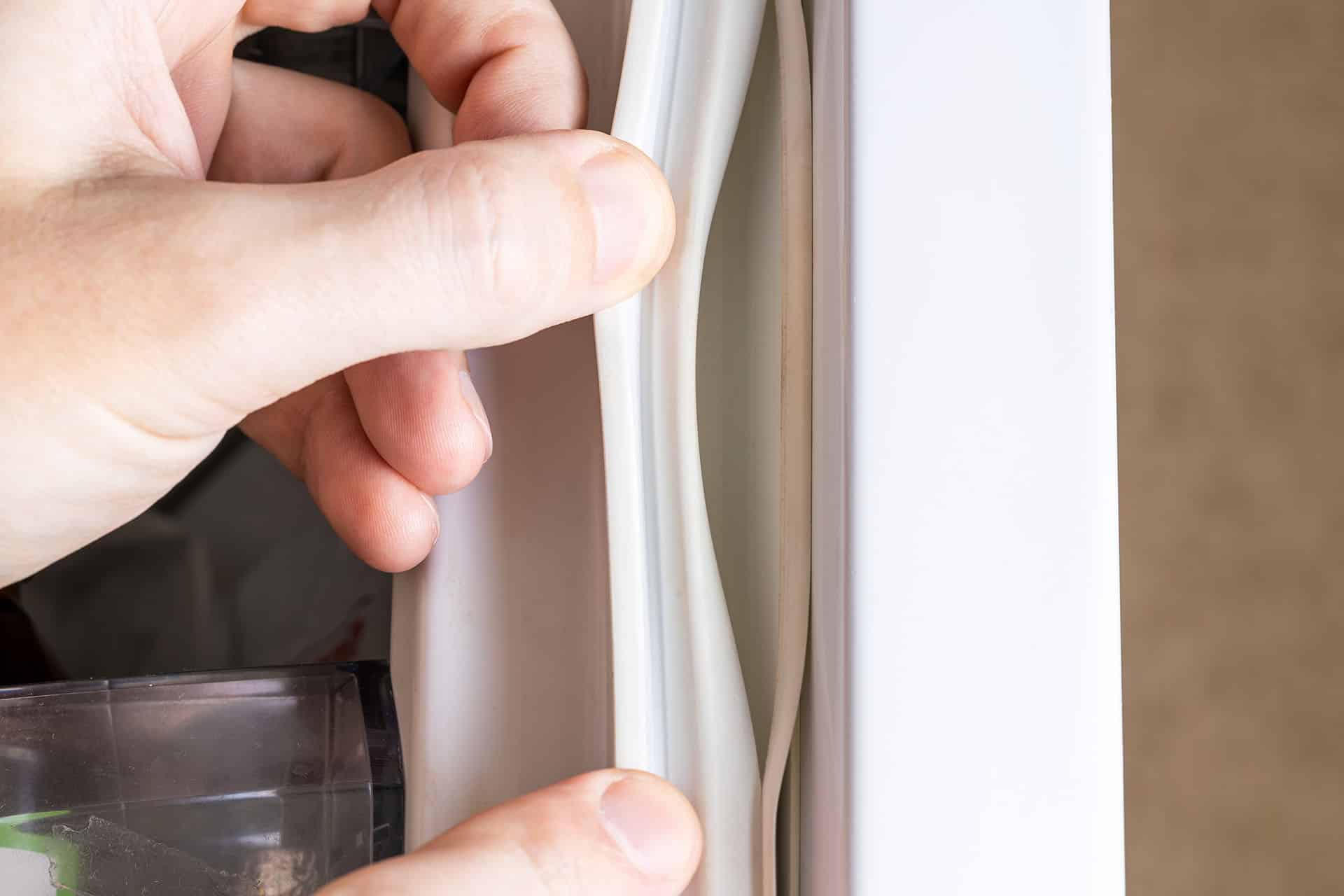
d) Check Seals on Fridge Door
Condensation outside your refrigerator-freezer indicates that the seals need to be changed. The main cause of energy loss in both refrigerators and freezers is leaky door seals. Poorly sealed doors allow the cold air to escape, increasing the workload on the appliance and lowering food quality.
Image source: checkatrade.com
Using the “paper” test, examine the door seals. On a sheet of paper, shut the freezer or refrigerator door. A properly sealed door will hold the paper tightly; if it comes loose or slides about readily, the seals need to be cleaned or replaced.
e) Don’t Store Hot Food in the Fridge
When you put hot food in the refrigerator, expect it to consume more power. This is because the hot food raises temperatures inside the fridge, making it work extra hard to make the fridge cooler. So before putting leftovers in the refrigerator, let it first reach room temperature.
f) Keep the Door Closed
Image source: chariotenergy.com
It’s easy to become preoccupied and leave the refrigerator door open while you take a quick break. The appliance will have to work harder to get the inside cool again because this lets all the cool air leave and all the warm air in. To lessen the strain on the appliance, try to limit the number of times you open the fridge door.
g) Upgrade to Energy Efficient Model
It may seem like stating the obvious, but energy efficiency in refrigerators has advanced significantly over time. You might easily pay twice as much to operate a highly effective model from five or ten years ago compared to a more recent model. If your refrigerator is quite old, consider replacing it.
Consider the fridge’s technological and physical qualities as you shop for one. Multi-door types typically use more energy than frost-free, freezer-top, and freezer-bottom variants. This is especially true if you won’t be able to maintain a fully stocked refrigerator.
What Affects the Power Consumption of a Fridge?
The actual energy consumption of your fridge or freezer will depend on many factors. These include:
a) Type
Your fridge type will determine whether it consumes more energy or less. For example, a commercial display fridge can be used ten times more than your bar fridge at home.
b) Size
Anything with a larger volume, such as side-by-side fridges, uses more electricity. Therefore, if you have a refrigerator with a large capacity, expect it to consume more energy. On the other hand, a mini fridge will use less power overall.
c) Location
The refrigerator will use more power in a warm area or poorly ventilated space.
d) Season
All refrigerators use more energy in summer than in winter as the surrounding temperature is higher.
e) Usage
The compressor has to work extra hard to keep things cool if the fridge door is kept open or opened frequently. It may also need to work harder to keep things cool if the fridge is empty rather than moderately supplied because opening the door causes more “cool air” to be replaced with “warm air.”
f) Temperature set point
The factory setting may keep the fridge cooler than needed.
g) Age
Old refrigerators are usually less energy efficient than new high-star-rated fridges. Therefore, if you have an old model, just know that it
Frequently Asked Questions On How Much Electricity a Refrigerator Uses
1. How much electricity does a refrigerator use daily?
A domestic fridge typically consumes between 100-250 watts. Over a whole day, a fried can consume 1-2 kilowatt-hour (kWh) of total energy usage. Check with its plug-in power meter to see how much electricity your fridge consumes daily.
2. Does a fridge use a lot of energy?
The average refrigerator does not consume a lot of energy. It can use approximately 1-2 kilowatts per hour.
3. How many units does a fridge use per day?
On average, a domestic fridge can use 1-2 kWh per day. If the 400 L fridge has over three stars, it will likely consume 1100kWh annually. Adding an ice maker to the refrigerator will increase its annual energy use by 81 kWh, raising your electricity cost.
4. Is it okay to turn off the refrigerator at night?
No, it is not advisable to turn off the fridge at night. The temperatures inside the fridge will rise, increasing the growth of harmful bacteria. As a result, the stored food items will become stale and unsafe for consumption.
5. Is it good to keep the fridge full or empty?
It is better to fill the fridge three-quarters full. Doing this ensures enough space for air circulation while also ensuring that the food inside is sufficient to help each other cool its neighbor down.